3D printing has revolutionized the dental industry, allowing even small practices to integrate this technology into their workflows with ease.
The advent of 3D printing has been a game changer in the world of dentistry. What was once a luxury reserved for only the largest and most well-funded dental practices and laboratories, 3D printers are now much more compact and affordable.
This has opened up a world of possibilities for smaller practices and labs, allowing them to integrate 3D printing solutions into their workflows with ease.
Brief History of 3D Dental Printing
Additive manufacturing has been around since the 1980s, but it wasn’t until the introduction of 3D printers in the 1990s that dentists began to see the benefits of this technology. With the ability to produce dental devices with more precision and speed than traditional CNC milling, 3D printers quickly became a go-to solution for dental professionals.
Initially, 3D printing was used primarily for making moulds for thermoforming, but advancements in hardware, software, and materials have led to a revolution in the dental industry.
Next-generation 3D printers are now capable of direct printing of dental products with superior materials and finish that require minimal post-processing.
Statistics on Dental 3D Printers
The advantages of incorporating 3D printers into dental operations are numerous. The faster turnaround time for oral devices and increased accuracy of dental models has helped to propel the clear aligner industry to a staggering $3.45 billion market size in 20211. And this is just the beginning.
While 3D printing is expected to continue to grow in other markets as well, manufacturers are already producing better 3D printers and materials specifically for the dental industry.
It’s clear that 3D printing has revolutionized dentistry, and dental professionals who embrace this technology are sure to reap the rewards.
Applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry
Dentists, orthodontists, and dental labs are using 3D printers to produce removable oral devices such as clear aligners, retainers, and nightguards.
They’re also using them for restorative dental treatments including crowns, bridges, denture bases, and implants.
3D printing is even being used to create surgical instruments like try-ins and surgical guides, as well as dental models for thermoforming or as diagnostic aids for cosmetic dentistry procedures, orthodontic treatment, or oral surgery.
Here’s a breakdown of some of the common applications of 3D Printing in Dentistry:
Replacing or repairing a damaged tooth
Dentists can use a small digital wand to scan a patient’s mouth, creating a 3D image of the teeth and gums, which is saved as a computer file. This computer-aided design (CAD) software enables the dentist to digitally design a tooth repair and print the finished product on a 3D printer.
Creating an orthodontic model
In the past, orthodontists relied on patients biting down on gooey, uncomfortable clay, which hardened into a mould, as the initial model for designing treatments for braces or Invisalign.
With 3D printing, orthodontists can use the same technology to scan the teeth, design an orthodontic appliance, and print the end result in-house.
Producing dental implants
The same process can be used to 3D print crowns, bridges, caps, dentures, and more. The only difference is the precise material used in the printing process.
Constructing surgical tools
Not only can 3D printers handle the dental implants themselves, but they can also 3D print the drill guides needed to complete certain dental procedures.
Typical Dental 3D Printing Process
A typical dental 3D printing begins with planning and designing. The planning and design of the dental component is followed by the preparation of the data, and the printing strategy is applied. The employed printing strategy acts as a blueprint for creating the denture.
Nesting, which refers to the arrangement and reorientation of components for all the printing parts, is then done, aligning as many components as close together as possible to save valuable post-processing time.
Once the printer is prepared for printing, the print file can be loaded straight from the CAM software.
Next, all the user has to do is start the print, and the system will create the part. After printing, the components are unpacked, and the excess powder is extracted, with the safe suction device. The collected powder can then be sieved and reused.
After printing, the components must be separated from their support structures, and for simple small components such as crowns, the objects can be separated directly from the build platform.
For large components, such as multi-unit bridges or partials, thermal post-treatment is mandatory.
Depending on the needs of the patients and their requirements, the components can then be polished and covered with the ceramic veneer, which is then colour-matched to the patient.
Benefits of 3D Printing Technology in Dentistry
3D printing technology has revolutionized many fields, and the field of dentistry is no exception. The advantages of 3D printing technology in dentistry are numerous, and they benefit both patients and dental professionals.
This section highlights the benefits of 3D printing technology in dentistry, including economy, speed, accuracy, precision, longer life, customized dental prosthetics, increased accuracy, reduced chair time, and a more efficient production process.
Economy and Good Management of Money and Resources
Traditional dental manufacturing processes, such as subtractive manufacturing, create more material wastage, and can lead to a dusty and dirty workplace for dental technicians.
In contrast, 3D printing technology creates less material wastage and provides a clean working environment.
Digital workflows in dentistry require less labour and lower costs, saving time and money for both dental professionals and patients. When a dentist needs a dental prosthesis, traditional methods involve sending the impression to a lab, which can take days or weeks to prepare. With 3D printing technology, the dentist can send a digital copy of the scanning to a 3D printing lab, which receives it in minutes. Hence, it becomes possible to start the work double-quickly.
Thus, 3D printing simplifies technicians’ workflows, reduces the amount of labour required, resulting in time and cost savings on both the lab’s and practitioner’s sides.
Speed, Accuracy, and Precision
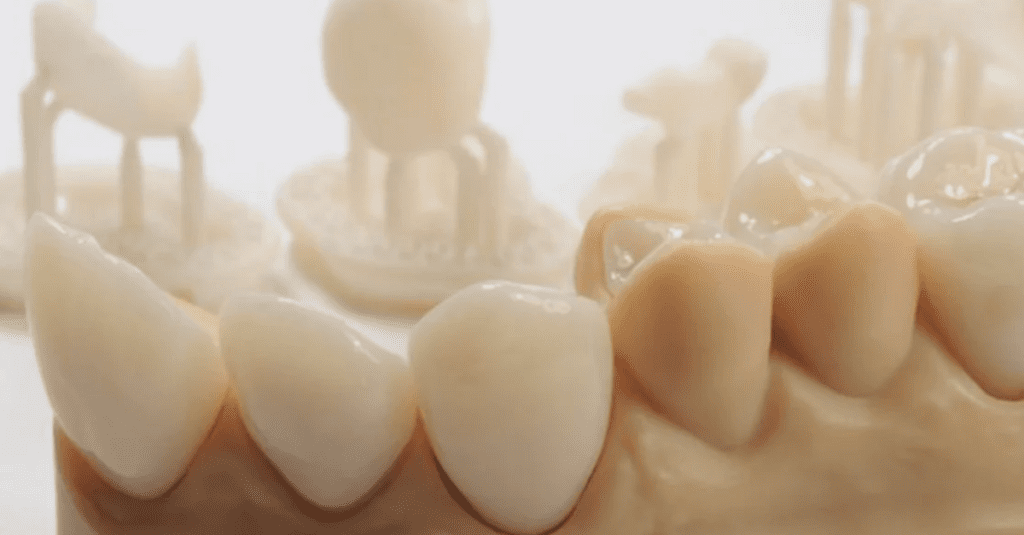

3D printing technology allows dentists to create various products from one machine, and different items can easily be printed on the same machine.
Accuracy is also improved since dental 3D printers convert digital images into physical objects by printing 16-micron-thick layers one on top of the other. This ensures that the prosthesis is prepared exactly according to the desired dimension.
These 3D printed devices are much more customizable and fit the patient better with no need for extensive trimming and polishing. Increased production capacity and more accurate final results benefit both dentists and patients, and 3D printing technology is particularly appropriate when it comes to dental services for children.
Customized Dental Prosthetics
3D printing technology allows dentists to create accurate digital models of patients’ teeth and gums and use these models to design and manufacture dental prosthetics that are tailored to each patient.
This results in restorations that fit perfectly and feel comfortable without needing multiple appointments and adjustments. Customized dental prosthetics made with 3D printing are also more durable and longer-lasting than traditional restorations.
Increased Accuracy
With the help of 3D printing, dental prosthetics are created using scanners, a digital model of the patient’s mouth, and a 3D printer. These three components work together to create an accurate digital model of the patient’s mouth that can be used to fabricate restorations efficiently.
Durability
3D-printed oral devices have a longer lifespan than traditional ones since they are more precise, and there are no structural defects or imperfections that can reduce their life.
Reduced Chair Time
The technology significantly reduces the number of appointments and dental visits needed for patients to receive their restorations.
3D printing eliminates the need for dental professionals to deal with multiple dental impressions, requiring less chair time.
3D scanning and printing allow dentists to scan, design, and print dental prosthetics in a single visit, which significantly reduces chair time. Also, using stone models to create wax moulds of the teeth is unnecessary before creating crowns or bridges. 3D scanning is also beneficial for multi-tooth restorations such as bridges and dentures.
FAQs on Dental 3D Printing
Q: What is the significance of 3D printing in dentistry?
A: The use of 3D printing technology in dentistry has the potential to improve healthcare by making it more accessible, effective, and affordable. 3D printing offers benefits like mass customization, consistent accuracy, efficiency, and cheaper alternatives to traditional manufacturing processes, thus revolutionizing the profession on a larger scale.
Q: What are the current industry trends in dental 3D printing?
A: Dental 3D printing is an emerging technology, and the current industry trends include increasing adoption of intraoral 3D scanners, milling machines, and the development of custom dental implants, clear aligners, and prostheses.
Q: What are some jobs that can be done with 3D printing in dentistry?
A: 3D printing technology can be used to create dental models, surgical guides, orthodontic aligners, temporary and permanent crowns, bridges, and dentures. It can also be used to develop custom dental implants and prosthesis for maxillofacial surgeries.
Q: What are the technical advantages of 3D printing in dentistry?
A: The technical advantages of 3D printing in dentistry include mass customization, consistent accuracy, efficiency, cheaper alternatives, and complexity for free. These benefits have made 3D printing a preferred alternative to traditional manufacturing processes in dentistry.
Q: Which companies are currently operating in the dental 3D printing space?
A: Several companies are actively involved in the dental 3D printing space, including Stratasys, 3D Systems, EnvisionTEC, Formlabs, Carbon, and others. These companies offer a range of 3D printing hardware, software, and materials that dental professionals can use.
Q: Why is the use of 3D printing technology crucial in dentistry?
A: Dental service is a luxury item, and many people do not receive dental care due to financial constraints, inadequate insurance coverage, or fear of dental procedures.
3D printing technology has the potential to make dental healthcare more accessible, affordable, and effective. It can also improve the quality of life of those who require dental care by offering custom solutions that are catered to individual needs.
Q: What are some of the major trends in Dental 3D Printing?
A: There are several major trends in dental 3D printing, including 3D printing for rapid prototyping, decreasing reimbursement for dental care, an increasing supply/demand gap for dental care, a shift in dental lab businesses to dental clinics, the emergence of new business models, the democratization of the clear aligner business, point-of-care manufacturing, the rise of robotic labs and AI/ML, and digital outsourcing.
Q: What jobs are being done with 3D printing in dentistry?
A: There are many existing and new applications of 3D printing in oral health. The industry can be organized by dental subspecialties, including general dentistry, oral surgery, endodontics, prosthodontist, periodontics, and orthodontics.
The surgical-based subspecialties, such as dental implantology, dental surgery, and orthodontics, are taking a lead in both research and commercialization of dental 3D printing services and products.
Q: How are clinics and labs responding to the changing dental landscape?
A: As more 3D printing adoption occurs, clinics and labs are merging into one entity to enable point-of-care delivery, streamline the digital workflow for clear dental, and democratize the clear aligner business.
Dental clinics have also begun producing in-office dental devices and setting up workflows that are friendly to private practices.
Q: What is the driving force behind the changing dental landscape?
A: The consumer is the strongest driving force in the dental market. Other areas in dental markets are also influenced by consumer demands.
New technologies enabling point-of-care delivery, a shrinking dental lab technician workforce, cost pressure, and a more consumer-driven market are some of the driving forces behind the changing dental landscape.
Q: How is AI/ML influencing the dental industry?
A: Artificial intelligence and machine learning strategies are being developed at every step of the digital workflow to optimize solutions in the dental industry. Robotic labs are also emerging to combat the shrinking workforce of lab technicians.
Q: What is the democratization of the clear aligner business?
A: The democratization of the clear aligner business refers to the streamlining of the digital workflow for clear dental with a 3D scanner, CAD/CAM, and 3D printing.
This process is on its way to taking over 90% of the market where you can get it at local CVS, leaving more complex cases to dental offices and traditional metal-wired braces.
Q: What is point-of-care manufacturing in dentistry?
Point-of-care manufacturing in dentistry refers to the production of in-office dental devices. While the medical community is still debating on if a hospital can act as a manufacturer, dental clinics have already begun producing in-office dental devices.
Q: What is digital outsourcing in dentistry?
A: Digital outsourcing in dentistry refers to outsourcing the design process for dental offices that want to keep manufacturing in-house.
It is likely that a hybrid of in-house and outsourced design and 3D printing customized for each practice is needed to optimize the solution in the end.
References
- Clear aligners market size, share, growth: Global report [2029] (2022) Clear Aligners Market Size, Share, Growth | Global Report [2029]. Available at: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/clear-aligners-market-101377
The information and viewpoints presented in the above news piece or article do not necessarily reflect the official stance or policy of Dental Resource Asia or the DRA Journal. While we strive to ensure the accuracy of our content, Dental Resource Asia (DRA) or DRA Journal cannot guarantee the constant correctness, comprehensiveness, or timeliness of all the information contained within this website or journal.
Please be aware that all product details, product specifications, and data on this website or journal may be modified without prior notice in order to enhance reliability, functionality, design, or for other reasons.
The content contributed by our bloggers or authors represents their personal opinions and is not intended to defame or discredit any religion, ethnic group, club, organisation, company, individual, or any entity or individual.

